Bone Collector
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 65099 Accepted Submission(s): 27122
Many years ago , in Teddy’s hometown there was a man who was called “Bone Collector”. This man like to collect varies of bones , such as dog’s , cow’s , also he went to the grave …
The bone collector had a big bag with a volume of V ,and along his trip of collecting there are a lot of bones , obviously , different bone has different value and different volume, now given the each bone’s value along his trip , can you calculate out the maximum of the total value the bone collector can get ?

The first line contain a integer T , the number of cases.
Followed by T cases , each case three lines , the first line contain two integer N , V, (N <= 1000 , V <= 1000 )representing the number of bones and the volume of his bag. And the second line contain N integers representing the value of each bone. The third line contain N integers representing the volume of each bone.
One integer per line representing the maximum of the total value (this number will be less than 2
31).
1 5 10 1 2 3 4 5 5 4 3 2 1
题目大意:有一个骨头收集者,他有一个容量为V的包,他要收集N根骨头,每根骨头拥有它的价值Valu和占用体积Vol,求最优解。
这是个简单的01背包问题,核心算法就是:F[i,v] = max{F[i − 1,v],F[i − 1,v − C i ] + W i } 具体的解释请看我的另一片博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/William-xh/p/7305877.html
主要就是还是要进行判断,如果背包放得下的话,那就是要看我放还是不放;如果是放不下的话,那就是不放。
这题我是用二维数组解的,一位数组那个代码还没有研究过,就也还没写过。之后要是写的话就码上来。
#include #include #include #include #include #include
然后在此进行一位数组的解释,这边有一个讲的还是比较清楚的:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_32036091/article/details/51301912
且说小Ho搞清楚了计算方法,正在埋头苦写代码,在一旁看他写代码的小Hi是在看不下去了,决定再指点指点小Ho:“小Ho啊!”
“怎么了?”小Ho眼睛盯着屏幕,望都没望小Hi一眼。
“你现在是不是需要开一个N * M大小的二维数组best,来记录求解出的best值呀?”
小Ho终于有了点反应,抬起头来说道:“是啊,怎么了?“
“我有办法不用开这么大空间哦~”小Hi笑嘻嘻道:”可我就是不告诉你!”
“诶,别这样,我请你吃雪糕!”小Ho一听就急了,连忙许下了报酬。
“开玩笑啦~”小Hi也是随便逗了逗乐子就没继续:“你想想,在i已经是10以上的时候,best(5, j)这样的值还有用么?”
“没有用了……你是说,我并不需要在内存中存下来所有的best(i, j),没有用了的值都可以不进行保存……也就是说,实际上只要开一个2*M大小的数组就可以了,然后像这样的方式进行来回的计算,是不是就可以了?”

“是的呢!但是还可以更少哦~让我来写这个程序的话,我只需要开一个M大小的一维数组就可以了”小Hi自信的说道:“你想想,如果我按照j从M到1的顺序,也就是跟之前相反的顺序来进行计算的话。另外根据我们的状态转移方程,可以显然得出如果状态(iA, jA)依赖于状态(iB, jB),那么肯定有iA = iB+1, jA>=jB。所以不难得出一个结论:我在计算best(i, j)的时候,因为best(i, j+1..M)这些状态已经被计算过了,所以意味着best(i - 1, k),k=j..M这些值都没有用了——所有依赖于他们的值都已经计算完了。于是它们原有的存储空间都可以用来存储别的东西,所以我不仿直接就将best(i, j)的值存在best(i-1, j)原有的位置上,就像这样。”
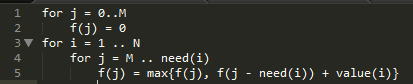
“原来还可以这样!这样一处理,不仅空间复杂度小了很多,代码也很好看了呢!”小Ho开心道。
“那你还不去写?”
然后,我在这边附一张自己的演示图:
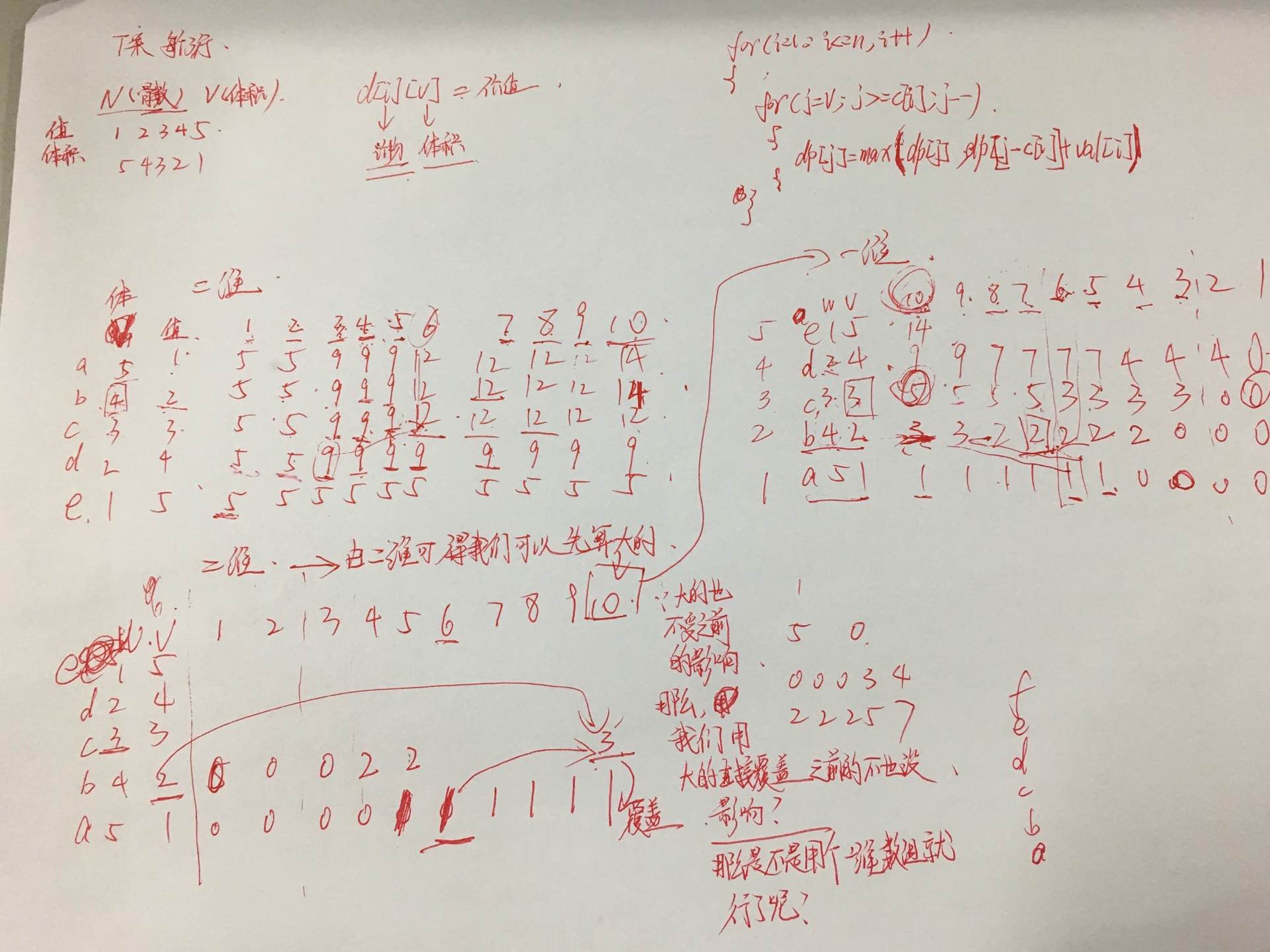
然后,根据你在纸上换算的过程,你可以得到一个核心算法:dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-vol[i]]+value[i]);
其实一维数组的核心就在于:1.从大到小进行计算 2.对之前的数据进行覆盖。
然后附上代码:
#include #include #include #include #include #include



